First Functional Battery free Cellphone – Zero Power
A cellphone that needs no battery which is a primary jump forward in moving beyond chargers, cords and dying phones has been considered by the scientists of University of Washington.
On the contrary the phone tends to gathers the few microwatts of power it tends to need from ambient radio signals or light. Their project is inclined to recognise speech, motivate the phones and then adjust between up link and down link conversations, in real time.
Their system is said to elevate transmission as well as reception of speech and at the same time harvest power that empowers the battery-free cellphone to function constantly. Skype calls had also been made by the group by utilising the battery-free phone, representing that the model made of commercial, off-the-shelf component could obtain as well as convey speech and communicate with a base station.
The new technology is said to be detailed in a paper which has been published on July 1 in the Proceedings of the Association for Computing Machinery on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies.
Co-author Shyam Gollakota, a junior professor in the Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering at the UW had stated that they have built what they believe is the first functioning cellphone which tends to consume almost zero power.
Convert Analog Signals into Battery Power
For the purpose of accomplishing really low power consumption desired for running a phone by harvesting energy from the environment, they had to fundamentally rethink how these devices are designed.
It is said that the team of UW computer scientists and electrical engineers had wiped out a power-hungry step in utmost current cellular transmissions converting analog signals which tend to convey sound into digital data which a phone can comprehend. This process tends to consume plenty of energy that has been difficult in designing a phone which could be dependent on ambient power sources.
The battery-free cellphone instead is inclined to take benefit of tiny vibrations in the microphone or speaker of the phone that takes place whenever a person seems to talk in a phone or listens to a call.
The components are linked to an antenna which tends to convert that motion into alterations in standard analog radio signal emitted through a cellular base station and this process is needed to encode speech patterns in reflected radio signals in a manner that utilises practically no power. In order to convey speech, the phone is said to utilise vibrations from the microphone of the device to encode speech patterns in reproduced signals.
Convert Programmed Radio Signals – Sound Vibration
To obtain speech, it converts programmed radio signals to sound vibration which are picked up by the speaker of the phone. In the model device, the user presses a button in order to switch between these two `transmitting’ and `listening’ modes.
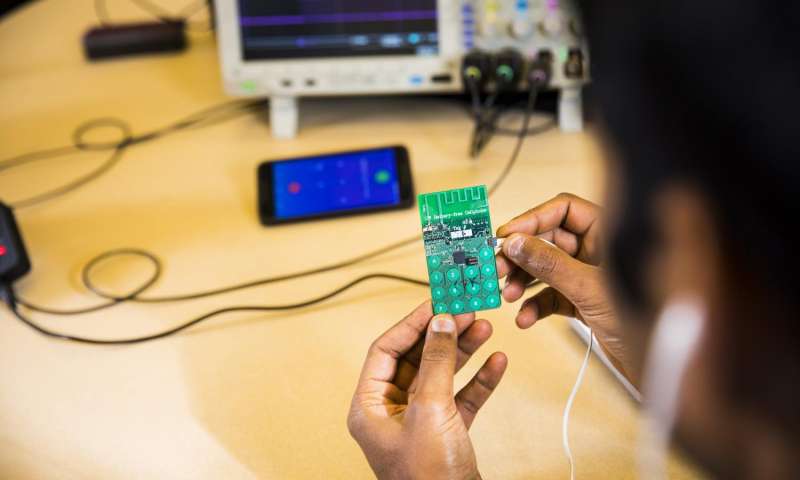
The team established that the prototype could perform basic phone functions in transmitting speech as well as data and receiving user input through buttons, by utilising regular components on printed circuit board. The researcher had been in a position of getting inward calls, dial out and place callers on hold with the battery-free phone by utilising Skype.
Faculty chief Joshua Smith professor in the Allen School as well as the UW’s Department of Electrical Engineering had commented that `the cellphone is the device they depend on presently and if there was one device you would want to be able to use without batteries, it is the cellphone. The proof of concept we have developed is exciting presently and we think it could impact the daily devices in the near future’.
The team had designed a custom-based station for the purpose of transmitting and receiving the radio signals. However the same technology possibly could be integrated into standard cellular network infrastructure or Wi-Fi routers which is now generally utilised in making calls.
Ambient Energy Sources for Battery
Co-author, Vamsi Talla, who had been a former UW electrical engineering doctoral student as well as Allen School research associate, had stated that `you could imagine in the future that all cell towers or Wi-Fi routers could come with our base station technology embedded in it. And if each household has a Wi-Fi router in it, they could get battery-free cellphone coverage everywhere’.
The battery-free phone tends to yet need a small volume of energy in order to perform some kind of processes. The prototype tends to have a power budget of 3.5 microwatts. The researchers of UW had established how to yield this small quantity of energy from two dissimilar types of sources.
The battery-free phone model is said to operate on power got together from ambient radio signals, which has been transmitted by a base station up to about 31 feet away. The device was capable of communicating with a base station which had been 50 feet away by utilising power harvested from ambient light with a tiny solar cell which had been approximately the size of a grain of rice.
A lot of other battery-free technologies which tend to depend on ambient energy sources, such as the temperature sensors or an accelerometer, conserve power together with intermittent operations.
Streaming Video – Battery-Free Cellphone
They are said to take a reading and thereafter tend to `sleep’ for a minute or two when they have harvested adequate energy for performing the next task. In contrast, a phone call is said to need the device for operation on a continuous basis for as long as the conversation seems to last.
Bryce Kellogg, co-author, a UW electrical engineering doctoral student had commented that one cannot say hello and wait for a minute for the phone to go to sleep and harvest adequate power to keep on transmitting which has been the biggest challenge. The amount of power one can really collect from ambient radio or light is on the order of 1 or 10 microwatts.
Hence a real-time phone operation tends to be really hard in achieving without developing a completely new approach for transmitting and receiving speech. The research team then planned to aim on making some enhancement on the operating range as well as encrypting conversation on the battery-free phone, in order to make them safe and sound.
The team is said to be working on streaming video over a battery-free cellphone as well as make some additions of visual display feature to the phone utilising low-power E-link screens.